Intermittent fasting (IF) has surged in popularity as a powerful approach to weight management, metabolic health, and even longevity. But is it the right strategy for everyone? In this comprehensive guide, we explore the science-backed benefits, the potential risks, and how factors like circadian rhythm, insulin sensitivity, and fasting protocols like the 16:8 fast can influence your results. You’ll also discover how intermittent fasting fits into a healthy lifestyle, what pitfalls to avoid, and how to customize it to your personal needs
🕐 What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting isn’t about what you eat, but when. It cycles between periods of eating and fasting, aiming to sync with your body’s natural metabolic processes. It’s less of a diet and more of a structured eating pattern.
Common Methods of Intermittent Fasting:
- 16:8 Fast: Fast for 16 hours and eat within an 8-hour window.
- 5:2 Diet: Eat normally five days a week, and restrict calories to around 500–600 for two non-consecutive days.
- Alternate-Day Fasting: Fast every other day, either completely or with minimal caloric intake.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: A 24-hour fast once or twice per week.
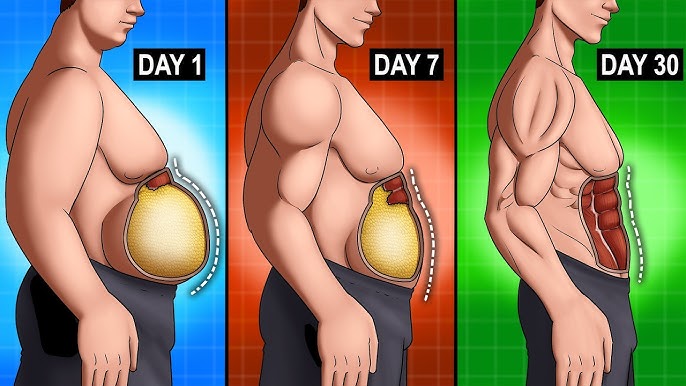
These methods aim to improve metabolic health by giving your body a break from constant digestion and insulin spikes, allowing it to shift into fat-burning and repair mode.
🌞 The Role of Circadian Rhythm in Intermittent Fasting
Your circadian rhythm is your body’s internal clock that regulates sleep, hormone release, digestion, and metabolism. Eating in alignment with your natural rhythm—i.e., during daylight hours—can significantly enhance the benefits of intermittent fasting.
Why Circadian Fasting Works:
- Boosts insulin sensitivity earlier in the day when the body is more receptive to nutrient absorption.
- Improves sleep quality when meals are consumed earlier, reducing late-night digestion.
- Enhances metabolic efficiency by syncing eating with energy and hormone peaks.
- Reduces late-night cravings, which are linked to poor dietary choices and weight gain.
📌 Pro Tip: Align your eating window during daylight hours, such as 10 AM to 6 PM, to maximize metabolic and hormonal benefits.
⚖️ Key Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
| Benefit | How It Works | Backed By Science? |
|---|---|---|
| Improved insulin sensitivity | Reduces insulin levels during fasting, allowing cells to absorb glucose better | ✅ Yes |
| Fat loss & body recomposition | Promotes fat burning while preserving lean muscle mass | ✅ Yes |
| Enhanced metabolic health | Improves blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammation markers | ✅ Yes |
| Cellular repair | Fasting triggers autophagy, where the body cleans out damaged cells | ✅ Yes |
| Mental clarity | Stabilized blood sugar and ketone production improve focus | ✅ Yes |
| Simplicity | No calorie counting — just time-focused eating | ✅ Yes |
“Fasting gives your body a chance to reset. Think of it as metabolic housekeeping.”
⚠️ Who Should Be Cautious About Intermittent Fasting?
While many thrive on IF, it’s not ideal for everyone. Fasting can be taxing if not appropriately timed or if done excessively. The key is personalization.
🚫 Not Recommended For:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women (may affect milk supply and fetal development)
- People with a history of eating disorders (can trigger disordered patterns)
- Underweight individuals (BMI < 18.5)
- Those with adrenal fatigue or chronic stress
🤔 May Need Medical Supervision:
- Type 1 or Type 2 diabetics (due to insulin management)
- People with thyroid imbalances (fasting may impact hormone regulation)
- Individuals on food-sensitive medications
📌 Always consult a licensed healthcare provider before implementing fasting protocols.
⏳ 16:8 Fast: The Most Popular Protocol
The 16:8 method is widely regarded as the most practical and sustainable IF method. It allows for structure without sacrificing social or family meals.
✅ Sample 16:8 Fasting Schedule
| Time | Activity |
| 8:00 AM | Begin fasting (black coffee, herbal tea, or water allowed) |
| 12:00 PM | Break fast with a protein-rich lunch |
| 4:00 PM | Healthy snack with good fats and fiber |
| 7:30 PM | Dinner (balanced and nutrient-dense) |
| 8:00 PM | Start fasting again |
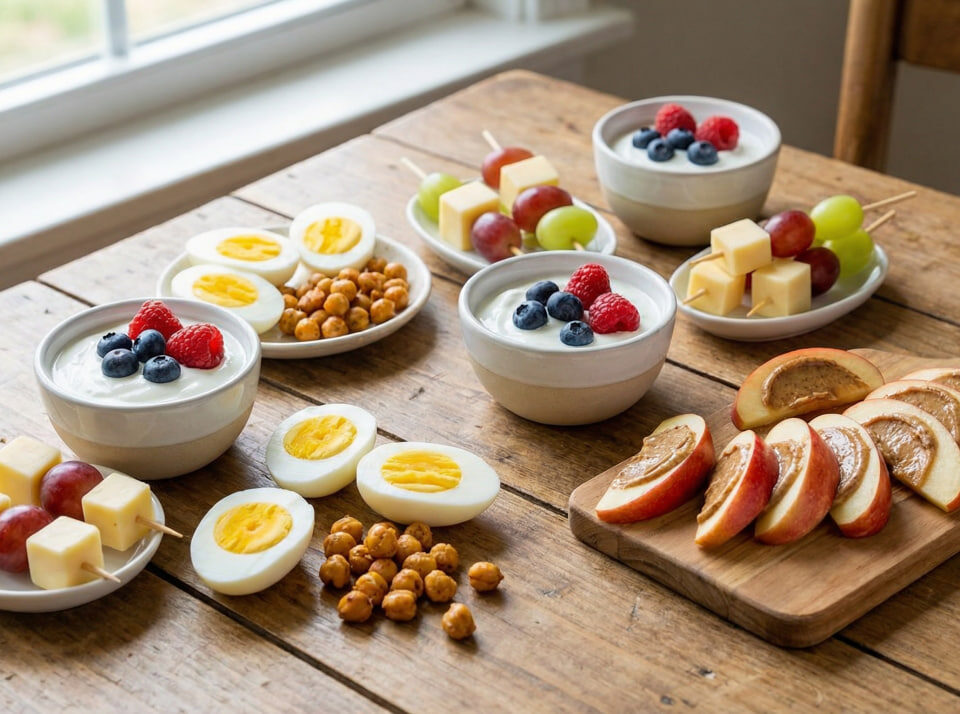
Ideal Meal Composition During Eating Window:
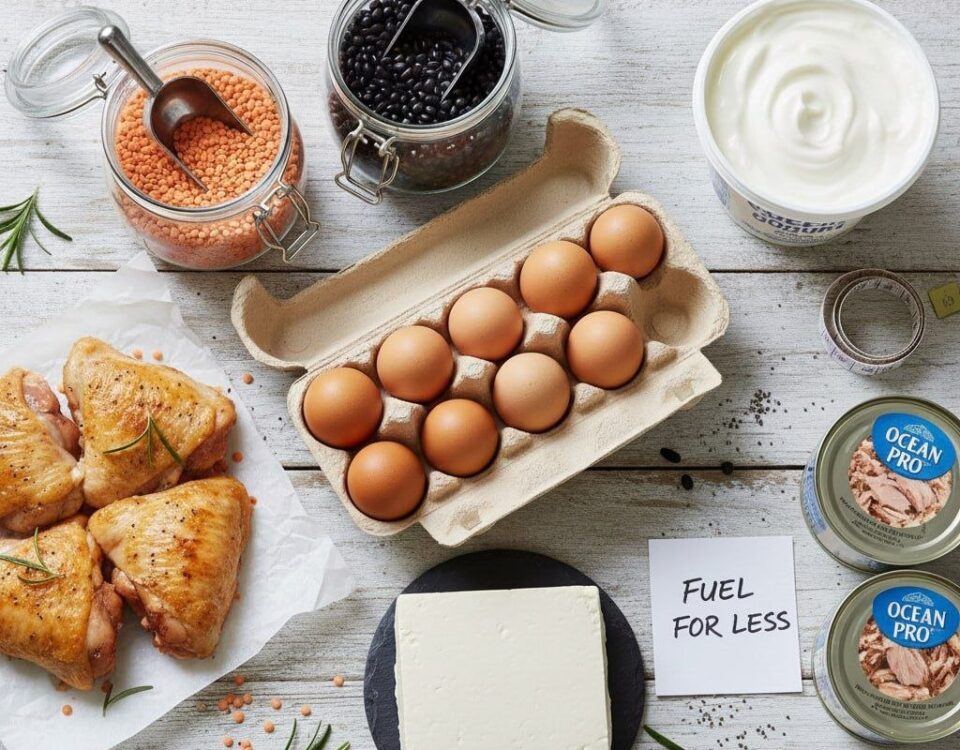
- Lean protein (chicken, tofu, eggs, legumes)
- Healthy fats (avocados, olive oil, chia seeds)
- Complex carbs (quinoa, lentils, sweet potatoes)
- High-fiber vegetables (spinach, cauliflower, peppers)
🔬 The Link Between Fasting and Metabolic Health
Intermittent fasting impacts several critical markers of metabolic health:
- Reduces fasting blood sugar and insulin resistance
- Improves HDL (good) cholesterol and lowers LDL (bad) cholesterol
- Reduces systemic inflammation (measured by CRP)
- Supports hormonal balance, including ghrelin and leptin
- Boosts mitochondrial function and cellular energy
- Increases production of BDNF for brain resilience
“Fasting doesn’t slow your metabolism — it recalibrates it.”
🧠 Mental Clarity & Cognitive Benefits
Many intermittent fasters report elevated mood, increased productivity, and sharper thinking. This is due to a combination of:
- Steady blood glucose reducing mental fatigue
- Ketone production offering clean brain fuel
- Reduced inflammation promoting better neurofunction
- Neuroplasticity stimulation through BDNF and autophagy
📌 Note: It’s normal to experience temporary fatigue or hunger during the adjustment period (typically 3–7 days).
🤔 FAQs About Intermittent Fasting
Is it okay to work out while fasting?
Yes! Moderate exercise (walking, yoga, weightlifting) is safe and often beneficial while fasting. For high-intensity workouts, some people prefer to eat a small meal first.
Can I drink coffee or tea during fasting?
Absolutely. As long as they are unsweetened and contain no calories. Black coffee and green tea can even enhance the fat-burning effects.
Will fasting slow down my metabolism?
No — short-term fasting (under 48 hours) may actually increase metabolic rate due to elevated norepinephrine levels.
Can I build muscle while intermittent fasting?
Yes, especially if strength training is combined with nutrient-rich meals during your eating window. Prioritize protein and post-workout nutrition.
What breaks a fast?
Any food or beverage containing calories will technically break a fast. Water, plain black coffee, and tea are safe.
📌 Final Verdict: Is It Smart for Everyone?
Intermittent fasting is a flexible, research-supported strategy that enhances metabolic health, boosts insulin sensitivity, and supports fat loss. It encourages intuitive eating, better food quality, and stronger biofeedback — but it’s not a silver bullet for everyone.
If you’re healthy, curious, and motivated, IF may be a smart lifestyle shift. Start slow, track your body’s response, and don’t ignore your biological cues. The smartest fast is one you can stick to sustainably.
🔗 Related Articles
- [What 1,500 Calories Looks Like: Smart Meal Plan Examples for Fat Loss]
- [Smart Plate Method: A Visual Guide to Portion Control]
- [Why Your Diet Isn’t Working: Top Hidden Weight Loss Blockers]
- [7-Day Smart Meal Plan for Beginners (with Grocery List)]
- [Circadian Fasting: Why Eating With the Sun May Be the Secret to Fat Loss]
- [How Fasting Affects Hormones: Insulin, Ghrelin & More Explained]
👉 Ready to take control of your health? Join Smart Diet Hub Membership for exclusive access to personalized fasting plans, live Q&A sessions, and expert nutritional guidance.